請設計一個程式,模擬一個基本的邏輯電路系統。這個電路系統由數個輸入端口、邏輯閘和輸出端口組成,您需要模擬電路中的訊號傳遞與閘的運算求出所有輸出端口的數值,並計算整個電路的最大延遲時間。
電路包含以下元件:
- 輸入端口 (Input Ports): 您將接收幾個二進制訊號,每個訊號的值為 0 或 1。這些訊號將用作電路的輸入。電路內共有 P 個輸入端口,編號為 1 到 P。
- 邏輯閘 (Logic Gates): 有四種類型的邏輯閘,分別為 「AND、OR、XOR 和 NOT 閘」。這些閘接收輸入訊號,並根據其功能進行運算。電路內共有 Q 個邏輯閘,編號為 P+1 到 P+Q。各種邏輯閘的運算規則如下:
- AND 閘 (AND Gate): 接收兩個輸入,如果兩個輸入皆為 1,則輸出為 1;否則輸出為 0。
- OR 閘 (OR Gate): 接收兩個輸入,如果至少有一個輸入為 1,則輸出為 1;如果兩個輸入皆為 0,則輸出為 0。
- XOR 閘 (XOR Gate): 接收兩個輸入,如果兩個輸入不相同,則輸出為 1;如果兩個輸入相同,則輸出為 0。
- NOT 閘 (NOT Gate): 僅接收一個輸入,並將其反轉。如果輸入為 1,則輸出為 0;如果輸入為 0,則輸出為 1。
- 輸出端口 (Output Ports): 最終結果將會從這些端口輸出,每個端口對應著某些閘的輸出值。電路內共有 R 個輸出端口,編號為 P+Q+1 到 P+Q+R。
請模擬這個電路系統,確定每個閘的輸出值,以及計算整個電路的最大延遲時間,最大延遲時間即訊號從輸入端口傳遞到輸出端口可能經過最多邏輯閘的數量。
範例測資
| 範例輸入 | 範例輸出 |
|---|---|
| 第一行包含四個整數,依序為 P、Q、R、M。P (1 <= P <= 103) 代表輸入端口的數量;Q (1 <= Q <= 5*104) 代表邏輯閘的數量;R (1 <= R <= 103) 代表輸出端口的數量;M 代表連接線的數量。 接下來一行有 P 個整數 v1, v2, …, vP,代表編號為 1 到 P 輸入端口的二進制值(0 或 1)。 接下來一行有 Q 個整數 t1, t2, …, tQ,代表編號為 P+1 到 P+Q的邏輯閘的類型 (1 為 AND、2 為 OR、3 為 XOR、4 為 NOT)。 最後的 M 行,每行包含兩個整數,代表連接線的起始端口和終端端口的編號。 每個輸入端口和邏輯閘的輸出會連到至少 1 個至多 20 個其他邏輯閘和輸出端口的輸入,且邏輯閘電路不會接出迴路。 | 第一行輸出一個整數,表示計算出的特定端口的最大延遲時間,測試資料保證最大延遲不高過 100。 第二行輸出 R 個二進制值(0 或 1),代表每一個輸出閘編號由小到大的輸出數值。 |
| 4 5 4 13 1 0 1 0 1 2 3 4 1 1 5 2 5 2 6 3 6 3 7 4 7 4 8 5 10 6 9 6 11 7 9 8 13 9 12 | 2 0 1 1 1 |
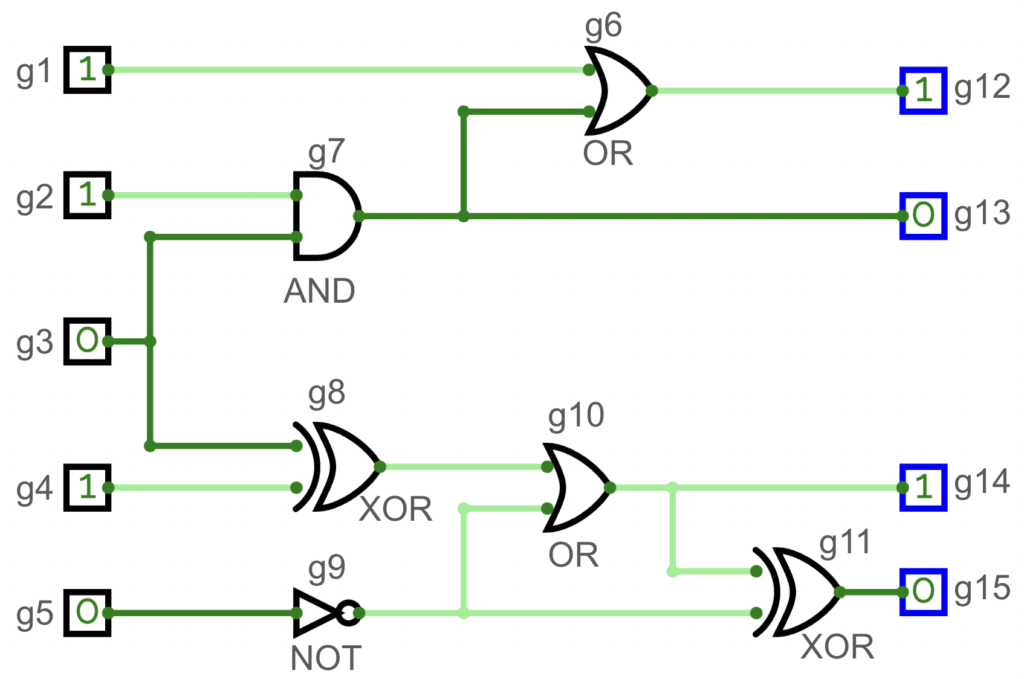
| 5 6 4 15 1 1 0 1 0 2 1 3 4 1 3 1 6 2 7 7 13 7 6 3 7 3 8 4 8 5 9 8 10 9 10 10 14 10 11 9 11 6 12 11 15 | 3 1 0 1 0 |
測資解釋
範例 1 解釋圖:
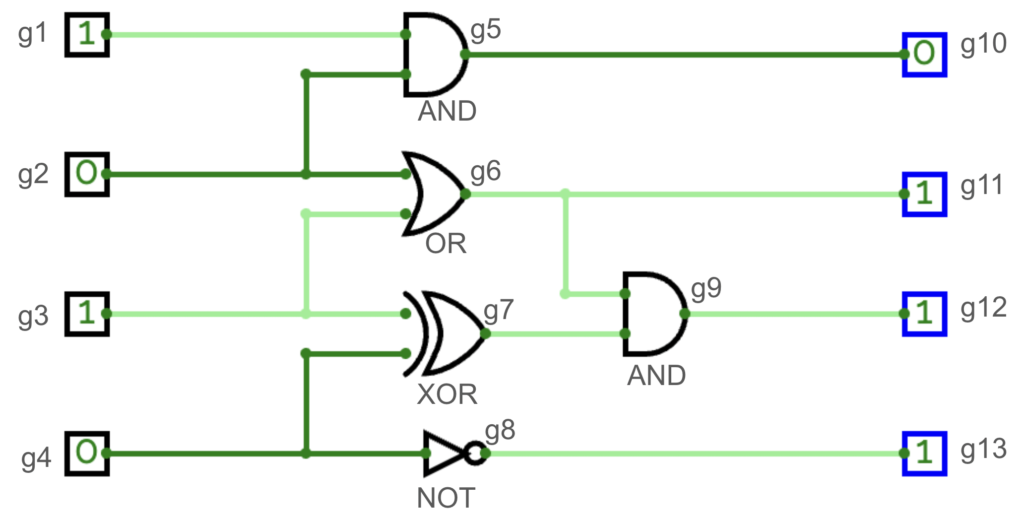
範例 2 解釋圖:
解題思路
可以使用一個 Struct 來存取每一個端點/邏輯端的數值,將資料都收到 Struct 中之後,使用 BFS 先跑輸入端點,將輸入端點的終點值的起點值存成目前的數字。經過判斷已經可以做邏輯端的運算後就可以將運算過後的值放到 Struct 中存輸出值的變數。延遲的部分只需判斷跑了幾次的 BFS 再 -1 即可。
範例程式碼-ZeroJudge M933: 邏輯電路
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
vector<int>from;
vector<int>to;
int output = -1;
int delay = 0;
int gate = -1;
};
int delay = 0;
vector<node>vec;
void BFS(vector<int>start)
{
if (start.size() == 0) return;
delay++;
vector<int>newStart;
for (int i = 0; i<start.size(); i++)
{
node vv = vec[start[i]];
for (int j = 0; j<vv.to.size(); j++)
{
int to = vv.to[j];
vec[to].from.push_back(start[i]);
if ((vec[to].gate == 4 && vec[to].from.size() == 1) || (vec[to].from.size() == 2))
{
newStart.push_back(to);
node point = vec[to];
int gate = vec[to].gate;
if (gate == 1)
{
if (vec[point.from[0]].output == 1 && vec[point.from[1]].output == 1)
{
vec[to].output = 1;
}
else vec[to].output = 0;
}
else if (gate == 2)
{
if (vec[point.from[0]].output == 1 || vec[point.from[1]].output == 1)
{
vec[to].output = 1;
}
else vec[to].output = 0;
}
else if (gate == 3)
{
if (vec[point.from[0]].output != vec[point.from[1]].output) vec[to].output = 1;
else vec[to].output = 0;
}
else
{
if (vec[point.from[0]].output == 0) vec[to].output = 1;
else vec[to].output = 0;
}
}
}
}
BFS(newStart);
}
int main() {
cin.sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int in, out, logic, line;
cin >> in >> logic >> out >> line;
vector<int>start;
for (int i = 0; i<in+out+logic; i++)
{
node tmp;
vec.push_back(tmp);
}
for (int i = 0; i<in; i++)
{
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
vec[i].output = tmp;
start.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = in; i<in+logic; i++)
{
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
vec[i].gate = tmp;
}
for (int i = 0; i<line; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
vec[a-1].to.push_back(b-1);
}
BFS(start);
cout << delay-1 << endl;
for (int i = in+logic; i<in+logic+out; i++)
{
cout << vec[vec[i].from[0]].output << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
//ZeroJudge M933
//Dr. SeanXD